We understand that calculating asphalt tonnage can feel overwhelming when you’re planning a paving project. Whether you’re a contractor preparing a bid or a property owner budgeting for repairs, we’re here to guide you through the process with proven methods and expert insights that ensure accuracy and prevent costly mistakes.
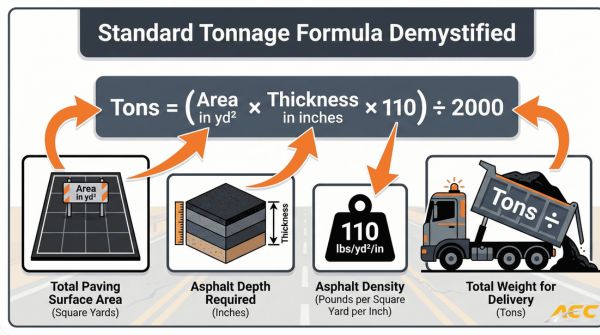
Figuring out asphalt tonnage is the process of calculating the exact weight of asphalt material needed for a paving project using area measurements, thickness requirements, and material density factors. The standard calculation formula is: Tons = (Area in square yards × Thickness in inches × 110 pounds per square yard per inch) ÷ 2000, though this varies by region and mix type.
According to Asphalt Institute Engineers Gierhart and Wielinski (2023), “Each extra 1% density results in at least 10% extra service life. This is a conservative estimate based on research. Fatigue performance improves 8.2-43.8% per 1% density increase, and rut resistance improves up to 66.3% per 1% density increase.” In 2024, SiteRecon AI demonstrated that contractors using AI-powered takeoff technology reduced their estimating time by 75% while winning 28% more profitable work through improved accuracy.
Key Takeaways
• Basic Formula: Calculate tonnage using Area (square yards) × Thickness (inches) × 110 lbs/yd²/in ÷ 2000 for standard dense-graded mixes
• Compaction Factor: Always add 10% to your calculated tonnage to account for material compaction during installation
• Regional Variations: Verify local spread rates with your state DOT, as they range from 88-112 lbs/yd²/in depending on location
• Measurement Accuracy: Use digital tools like GPS or AI takeoff software for 5-10% faster and more consistent area measurements
• Density Testing: Maintain 95% field density target using the formula: % Compaction = (field density ÷ maximum theoretical density) × 100
• Mix Type Adjustments: Apply material adjustment factors for specialty mixes – add 5-10% for Stone Matrix Asphalt, subtract 20% for Open-Graded Friction Course
• Verification Methods: Implement dual testing with gauges for process control and cores for acceptance verification
Understanding Your Project’s Full Scope
We recognize that accurate tonnage calculation forms the foundation of successful asphalt projects, affecting everything from material costs to project timelines. This comprehensive guide walks through each calculation step, from measuring your project area to adjusting for environmental factors and specialty mixes. We’ll explore proven formulas, industry-standard tools, and common pitfalls that can derail your estimates. By mastering these techniques, you’ll ensure proper material ordering, competitive bidding, and optimal pavement performance that delivers the 10% service life extension per 1% density improvement that research confirms.
Practical Tips for Immediate Application
• Start with a control strip before full production to establish baseline density and validate your tonnage calculations against actual field conditions
• Schedule deliveries accounting for the “tender zone” between 190°F and 230°F where asphalt becomes difficult to compact, adjusting tonnage timing to maintain optimal temperatures
Understanding how to accurately calculate asphalt tonnage sets the foundation for every successful paving project. With the right measurements, formulas, and verification methods in place, we can now explore the specific components that make these calculations work effectively.
What is asphalt tonnage and why does it matter?
Asphalt tonnage is the total weight of asphalt material required for a paving project, measured in tons. This measurement determines material orders, project costs, and pavement performance outcomes. The calculation follows the formula: Tons = (Area_ft² × Thickness_in × Density_lb/ft³) ÷ (12 × 2000). A simplified version uses: Tons = (Area_yd² × Thickness_in × Spread_Rate) ÷ 2000, where the industry standard spread rate is 110 pounds per square yard per inch of compacted thickness for dense-graded mixes. Metric calculations multiply cubic metres volume by 2.4 to get tonnes of asphalt. Accurate tonnage calculations ensure proper material ordering and optimal pavement density for long-term durability.
How is asphalt tonnage defined in paving projects?
Asphalt tonnage is calculated using the formula: Tons = (Area_ft² × Thickness_in × Density_lb/ft³) ÷ (12 × 2000). The simplified formula uses square yards: Tons = (Area_yd² × Thickness_in × Spread_Rate) ÷ 2000. The industry standard spread rate equals 110 pounds per square yard per inch of compacted thickness for dense-graded mixes. Metric calculations multiply cubic metres volume by 2.4 to get tonnes. These formulas account for material density and compaction factors essential for accurate project planning.
Why is it important to calculate asphalt tonnage accurately?
Accurate asphalt tonnage calculations directly impact pavement performance and project costs. Each 1% increase in mat density extends service life by at least 10%, according to conservative industry estimates. A 2019 NCAT study found that 1% density improvement increases fatigue performance by 8.2% to 43.8% and rut resistance by up to 66.3%. Delivery errors cost concrete and asphalt operations 3-5% of annual revenue on average. Manual estimating creates costly errors and lost bids, while software solutions reduce estimating time by 75-80%. An IDOT analysis of 219 asphalt paving projects revealed average cost overruns of 4% above bid price. These statistics demonstrate how precision in tonnage calculations protects profit margins and ensures pavement longevity through proper density achievement.
What key measurements are required to calculate asphalt tonnage?
Calculating asphalt tonnage requires three essential measurements: area, thickness, and density. Digital measurement tools reduce estimation time by 75% while improving accuracy over manual methods.
How do you measure the area (length and width) for asphalt projects?
Area measurement for asphalt projects uses digital tools that deliver 5-10% faster results than manual methods. SiteRecon AI technology cuts paving estimating time by 75% through automated asphalt tonnage and square footage calculations. GPS systems, drone imagery, and AI takeoff software provide consistent measurements across irregular project boundaries.
Highway projects express measurements as Tons/Project Station (T/sta) for direct comparison with plan sheets. Overall contract quantities use Tons/Mile (T/MI) measurements. These standardized units enable contractors to verify quantities against DOT specifications.

How do you determine the depth or thickness of asphalt needed?
The depth of asphalt needed depends on nominal maximum aggregate size (NMAS) specifications. Dense-graded mixtures require minimum lift thickness of 4 times the NMAS. Fine-graded mixtures need 3 times the NMAS minimum.
A typical ½” NMAS mix requires 2-inch minimum lift thickness. Fine-side ½” NMAS mixtures work at 1.5-inch thickness. The National Center for Asphalt Technology (NCAT) demonstrated successful compaction at 8-inch maximum lift thickness on their test track.
These thickness requirements ensure proper compaction and long-term pavement performance.
What units should you use for calculation accuracy?
Calculation accuracy depends on using standardized units and precision measurements. AASHTO T343 standard specifies 0.050 g/cm³ as the permissible standard deviation for asphalt mixtures. Single operator precision for bulk specific gravity shows 0.009 standard deviation with 0.025 acceptable range.
Multilaboratory precision testing reveals 0.013 standard deviation with 0.038 acceptable range. These precision standards ensure consistent tonnage calculations across different testing facilities and operators.
Accurate measurements form the foundation for reliable tonnage estimates that prevent material shortages and reduce project costs.
How do you convert area and thickness into asphalt tonnage?
Converting area and thickness into asphalt tonnage requires understanding the relationship between volume, density, and weight. The standard formula accounts for area in square feet, thickness in inches, and asphalt density in pounds per cubic foot. Accurate conversion ensures proper material ordering and prevents costly overruns or shortages on paving projects.
What is the standard formula for calculating asphalt tonnage?
The standard formula for calculating asphalt tonnage is Tons = (Area_ft² × Thickness_in × Density_lb/ft³) ÷ (12 × 2000). This formula converts cubic measurements to weight by dividing by 12 to convert inches to feet, then by 2000 to convert pounds to tons.
For highway projects, two miles of 24-foot-wide pavement with 2.5-inch intermediate and 1.5-inch surface lifts requires approximately 6,200 tons total. Parking lot calculations follow the same principle: 50,000 square feet at 2-inch depth equals 611 tons base calculation, plus 10% compaction factor for 672 tons required.
The formula accounts for material density and compaction, critical factors that affect final tonnage requirements.
How do you adjust calculations for irregularly shaped areas?
Irregularly shaped areas require specialized tools for accurate tonnage calculations. AI-powered takeoff tools provide precise calculations for complex geometries, helping contractors win 28% more profitable work through improved accuracy.
Software solutions such as OneCrew include automated calculations and property measurement tools specifically designed for irregular shapes. These tools eliminate manual calculation errors by automatically segmenting complex areas into measurable sections and applying the tonnage formula to each segment.
Digital measurement technology reduces estimation time while increasing bid accuracy for non-rectangular project areas.
What is the density of hot mix asphalt and why does it matter?
The density of hot mix asphalt directly determines tonnage calculations and pavement performance. Theoretical Maximum Specific Gravity (Rice Value) ranges from 2.400 to 2.700, with 2.500 as the common value for standard mixes.
Maximum Unit Weight calculation multiplies Rice value by 62.4 pounds per cubic foot. A 2.500 Rice value × 62.4 equals 156.0 PCF, with 95% compaction target yielding 148.2 PCF field density.
| Material | Attribute | Standard | Industry Context |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Rice Value Range (Gmm) | 2.400 – 2.700 | Industry standard range |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Common Rice Value | 2.500 | Typical design assumption |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Maximum Unit Weight | 156.0 PCF (2.500 × 62.4 lb/ft³) | Theoretical maximum density |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Target Field Compaction | 95% of maximum unit weight | Construction specification |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Target Field Density | 148.2 PCF | Performance benchmark |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Target Air Void Content | 3% – 7% | Performance specification |
| Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Critical Air Void Threshold | ≥ 8% | Durability limit |
Target air voids between 3-7% ensure optimal performance. At 8% or higher air voids, interconnected voids allow air and moisture permeation, reducing pavement durability significantly.
Understanding density variations helps contractors adjust tonnage calculations for different mix designs and achieve specified compaction levels during construction.
What tools and calculators can help you figure out asphalt tonnage?
Modern technology offers multiple solutions for calculating asphalt tonnage accurately. Digital tools eliminate manual calculation errors and reduce estimating time by up to 80%. The right combination of online calculators, specialized software, and verification methods ensures project success.
Are there online asphalt tonnage calculators?
Online asphalt tonnage calculators are web-based tools that instantly convert project dimensions into material requirements. Pro Asphalt Calculator provides calculations that automatically account for compaction factors, eliminating the need for manual adjustments. Quadratic HQ Asphalt Calculator includes density verification features to cross-check calculations against industry standards.
SiteRecon AI offers AI-powered takeoffs that reduce estimating time by 75%. The platform uses artificial intelligence to analyze project specifications and generate accurate tonnage calculations. These tools process complex geometries and irregular shapes that challenge manual methods.
Most online calculators require three inputs: area in square feet or yards, thickness in inches, and material density. Advanced calculators include options for different asphalt mix types, regional variations, and compaction factors.

How do software and mobile apps simplify tonnage calculations?
Software and mobile apps simplify tonnage calculations through automation, integration, and real-time data access. OneCrew reduces estimating time by 75-80% with automated calculations and QuickBooks Online integration. The platform eliminates double-entry errors and synchronizes estimates with accounting systems.
PavementSoft offers enterprise features including property measurement tools and mobile apps for approximately $99 per month. The software handles complex project geometries and multiple mix designs simultaneously. HCSS HeavyBid provides a Quick Pricing module specifically for heavy civil and DOT projects, incorporating historical cost data for accuracy.
Machine learning models now predict optimal bitumen content with R² values exceeding 0.98 accuracy. These algorithms analyze thousands of mix designs and field performance data to optimize tonnage calculations. Mobile apps enable field teams to verify calculations on-site and adjust for real-world conditions.
Integration capabilities connect estimating software with project management systems, material suppliers, and trucking logistics. This connectivity ensures tonnage calculations flow seamlessly through the project lifecycle.
What manual methods or spreadsheets can you use?
Manual methods and spreadsheets can calculate asphalt tonnage when digital tools are unavailable. C&R Paving recommends three steps: measure carefully, convert units to match, and apply density and compaction factors systematically. Spreadsheet templates automate formula calculations while allowing manual input verification.
Regional spread rate variations require adjustment in manual calculations. Illinois DOT specifies 112 pounds per square yard per inch for standard mixes. Tennessee DOT dense-graded mixes use 106 pounds per square yard per inch. Indiana DOT open-graded mixes require 100 pounds per square yard per inch.
| Source | Attribute | Specification | Year |
| Illinois DOT | Spread Rate | 112 lbs per square yard per inch (lbs/yd²/in) | State Specification |
| Tennessee DOT | Dense-Graded Rate | 106 lbs per square yard per inch (lbs/yd²/in) | State Specification |
| Indiana DOT | Open-Graded Rate | 100 lbs per square yard per inch (lbs/yd²/in) | State Specification |
| Standard Formula | Calculation Method | Area × Thickness × Density ÷ 2,000 (lbs to tons) | Industry Standard |
Excel formulas can replicate tonnage calculations with built-in error checking. Manual verification provides a backup when technology fails or for small projects where software costs exceed benefits.
The combination of online calculators, specialized software, and manual verification methods ensures accurate asphalt tonnage calculations across all project types and sizes.
What common mistakes occur when figuring out asphalt tonnage?
Common mistakes in asphalt tonnage calculations stem from incorrect density assumptions, measurement errors, and overlooking compaction factors. A 2019 study by the National Asphalt Pavement Association found that estimation errors account for 3-5% of annual revenue losses in paving operations.
What happens if you underestimate or overestimate tonnage?
Underestimating tonnage causes 10% material shortages requiring emergency deliveries and project delays. Emergency material orders typically cost 15-20% more than scheduled deliveries due to rush fees and logistics constraints.
Overestimating results in 10% excess material cost and waste disposal expenses. According to a 2021 EPA report on construction waste, asphalt disposal fees range from $30-75 per ton depending on regional regulations.
Using incorrect density values causes 2-5% systematic error across all project estimates. There are three critical density-related mistakes:
- Assuming 145 lb/ft³ when actual density is 150 lb/ft³
- Applying highway-grade density to parking lot mixes
- Ignoring temperature-adjusted density variations
Regional spread rate variations cause 2-12% error depending on mix type. Standard rates differ significantly:
| Source | Attribute | Value | Year |
| Illinois DOT | Dense-graded spread rate | 112 lbs/yd²/in | IDOT 2022 |
| Tennessee DOT | Dense-graded spread rate | 106 lbs/yd²/in | TDOT 2021 |
| Indiana DOT | Open-graded spread rate | 100 lbs/yd²/in | INDOT 2023 |
| Stone Matrix Asphalt | Specialty mix adjustment | +5-15% from standard | NAPA 2020 |
| Open-Graded Friction Course | Specialty mix adjustment | -20% from standard | FHWA 2019 |
Applying standard rates to specialty mixes causes 5-15% error for specialty applications. These tonnage miscalculations compound when contractors fail to verify mix-specific density values with suppliers before estimating.
How can errors in measurement affect the final result?
Measurement errors directly impact material requirements and project costs. Failing to account for 10% compaction during installation leads to project shortfalls.
Temperature effects not considered result in rework costs of 5-20% of material cost. A 2020 Asphalt Institute study on temperature sensitivity demonstrated that mix volumetrics change significantly between production and placement temperatures.
Specific gravity measurement precision affects air void calculations:
- Gmm change of ±0.01 results in ±0.4% change in air voids (Va)
- Gmb change of ±0.01 results in ∓0.4% change in Va and VMA
- Combined errors can shift air voids by ±0.8%, moving outside specification ranges
Digital measurement tools reduce these errors. According to a 2023 Construction Technology Report, contractors using GPS and drone surveying achieve 5-10% better accuracy than manual measurements. Understanding these error sources helps contractors implement quality control measures that prevent costly tonnage miscalculations affecting project profitability and performance.
How do project conditions impact the asphalt tonnage needed?
Project conditions significantly affect asphalt tonnage calculations through compaction rates and environmental factors. Understanding these variables ensures accurate material ordering and prevents costly shortages or overages during paving operations.
How does compaction or material loss affect calculations?
Asphalt typically compacts approximately 10% during installation. Contractors must set screed height at 1.25 times the final planned compacted thickness, accounting for a 25% roll-down factor. Open-graded mixtures require a 15% roll-down factor instead of 25%.
Specialty mixes demand different tonnage adjustments:
- Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA): 115-120 lbs/yd²/in (5-10% increase from standard)
- Open-Graded Friction Course (OGFC): 88 lbs/yd²/in (20% reduction from standard)
- Dense-graded standard mix: 110 lbs/yd²/in baseline
These variations occur because different aggregate structures and binder contents create unique compaction characteristics. Material loss during transport and placement adds another 1-2% to required tonnage calculations.
How do weather and temperature influence the amount of asphalt?
The tender zone occurs between 190°F and 230°F where mixture exhibits pushing and shoving under roller. Below 175°F, compaction becomes ineffective, resulting in low density and potential tonnage waste.
Temperature parameters for optimal paving include:
- Ideal paving temperature: 50°F and rising
- Minimum surface temperature: 40°F
- Mix temperature range: 275°F to 300°F for workability
According to aging studies, short-term aging increases dynamic modulus by 9.3%, long-term aging by 44.8%, and ultra-long-term by 57%. Wet-dry cycles affect material integrity—14 cycles decrease dynamic modulus by 10.8%, while 21 cycles decrease it by 16.5%.
Cold weather requires faster paving operations and potentially higher initial tonnage to compensate for rapid cooling. Hot weather extends workability but may increase material oxidation, affecting long-term tonnage requirements for maintenance.
How should you approach figuring out asphalt tonnage with help from an expert?
Figuring out asphalt tonnage with expert help combines professional verification methods with advanced software solutions. Professional contractors achieve 75-80% reduction in estimation errors through systematic approaches. The following expert methods and key principles ensure accurate tonnage calculations.
Can Asphalt Coatings Company help you accurately determine asphalt tonnage?
Asphalt Coatings Company helps accurately determine asphalt tonnage through dual-method verification and correlation testing. Professional contractors use nuclear and non-nuclear gauges for real-time density control paired with core samples for defensible acceptance. Experts establish correlation factors between plant testing and field testing for each specific project.
Industry professionals recommend establishing baseline density via control strip before production begins. This approach provides reference values for ongoing quality control. Contractors using professional software solutions achieve 75-80% reduction in estimation errors compared to manual methods.
Expert verification ensures accuracy through systematic testing protocols and proven methodologies. Professional guidance eliminates common calculation mistakes while optimizing material ordering.
What are the key takeaways on how to figure out asphalt tonnage?
The key takeaways for figuring out asphalt tonnage are formula application, compaction accounting, and technology implementation. Use the formula: Tons = (Area_yd² × Thickness_in × 110 lbs/SY/in) ÷ 2000 for standard dense-graded mixes. Account for 10% compaction by multiplying calculated tonnage by 1.10.
Verify regional spread rates with state DOT specifications, which vary 88-112 lbs/SY/in. Apply Material Adjustment Factors for specialty mixes:
• Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA): +5-10%
• Open-Graded Friction Course (OGFC): -20%
• Standard dense-graded: baseline
• Fine-graded mixtures: verify local specifications
Maintain 95% field density target using the formula: % Compaction = ρ_field ÷ ρ_Gmm × 100. Technology tools reduce errors significantly—AI takeoff software cuts estimating time 75% and wins 28% more profitable work. Implement dual testing methods using gauges for process control and cores for acceptance verification.
These proven methods ensure accurate tonnage calculations while minimizing material waste and project delays through systematic verification.